Several tree species in Asia are considered endangered due to habitat loss, illegal logging, climate change, and other environmental pressures. Some of these species include:
Condori Wood (Adenanthera pavonia)
Adenanthera pavonina, otherwise known as condori wood, cardinalier, red bead tree, red sandalwood tree or coral tree, is a species of flowering tree in the family Mimosaceae, or Fabaceae (a subfamily of Mimosoideae).

These trees are native to southern Asia and northern Australasia. They are best known for their attractive, bright red seeds and pinnate leaves. This tree is useful for nitrogen fixation, and it is often cultivated for forage. The young leaves can be cooked and eaten. The raw seeds are toxic, but may be eaten when cooked. Both the leaves, bark and seeds are used in traditional mediciines.
The species is threatened by overexploitation and habitat loss.
Dipterocarps (Dipterocarpus)
Dipterocarps are a family of tropical hardwood trees known as Dipterocarpaceae. They are primarily found in Southeast Asia, including countries like Indonesia, Malaysia, Thailand, and the Philippines. These trees are highly valued for their durable timber, which is used in construction, furniture, and plywood.
Dipterocarps are also ecologically significant, forming dominant canopies in many lowland rainforests and playing a vital role in forest dynamics and biodiversity. They typically grow tall, often exceeding 50 meters (around 165 feet), and produce distinctive seeds with wing-like structures that aid in wind dispersal.
Many species of dipterocarps, which are crucial in tropical rainforest ecosystems, are threatened due to deforestation and logging practices.
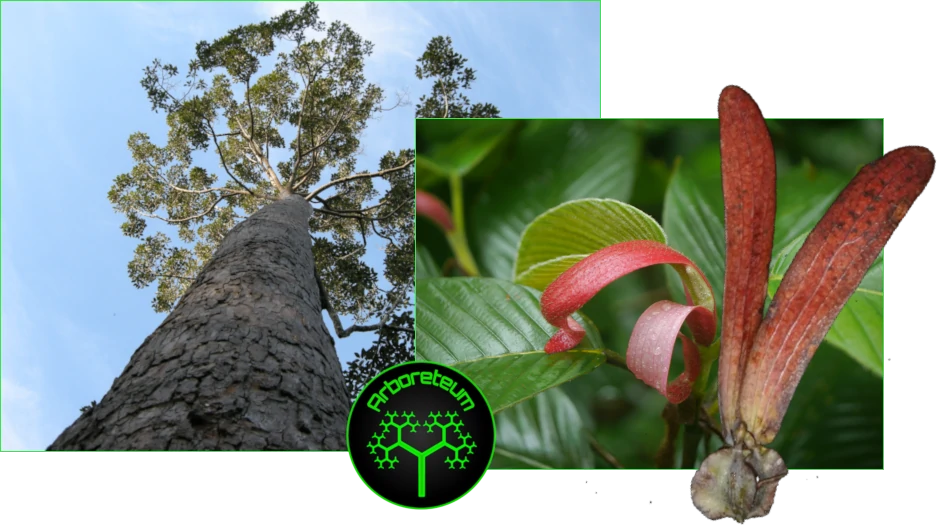

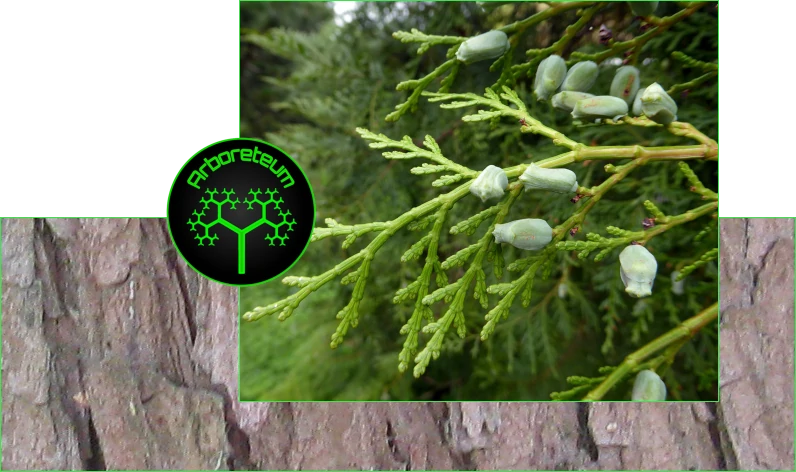
Fujan Cypress (Fokienia hodginsii)
Fokienia hodginsii is a species of coniferous tree belonging to the Cupressaceae family. It is commonly known as the Fujian cypress or Hainan cedar. This species is native to parts of Southeast Asia, including southern China, Vietnam, and Hainan Island.
Fokienia hodginsii is valued for its durable, aromatic wood, which is used in construction, furniture, and traditional carpentry. The tree typically grows in mountainous, subtropical forests and can reach significant heights. Due to overharvesting and habitat loss, it is considered vulnerable or near-threatened in some regions, leading to conservation efforts to protect this species.
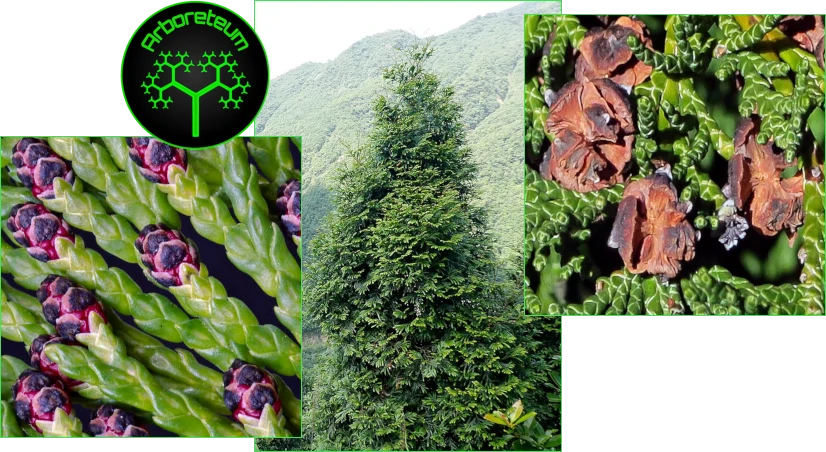

Happy Tree (Camptotheca acuminata)
Camptotheca acuminata, commonly known as the Happy Tree or Thorne Tree, is a species of flowering plant in the family Nyssaceae. It is native to China and is notable for its medicinal properties. The plant produces compounds called camptothecin derivatives, which have been researched for their potential as anticancer agents. These compounds are the basis for several chemotherapy drugs, such as topotecan and irinotecan. Besides its medicinal uses, Camptotheca acuminata is also valued for its ornamental appeal due to its attractive foliage and flowers.
The Camptotheca acuminata population is considered vulnerable due to habitat loss and overharvesting.

 Himalayan Yew (Taxus wallichiana)
Himalayan Yew (Taxus wallichiana)
Taxus wallichiana, commonly known as the Himalayan yew, is a species of coniferous tree in the family Taxaceae. It is native to the Himalayan region, including countries like India, Nepal, Bhutan, Myanmar, and parts of southwestern China. The tree typically grows in mountainous areas at elevations of 1,000 to 4,000 meters.
It is an evergreen conifer with a slender, conical shape. The foliage consists of needle-like leaves that are dark green on the top and have a lighter underside. Traditionally, parts of the tree have been used in medicine, especially in traditional Chinese medicine. Notably, compounds derived from Taxus species, including Taxus wallichiana, are sources of the anti-cancer drug paclitaxel (Taxol).
Due to overharvesting and habitat loss, some populations are under threat, and conservation efforts are important to preserve this species.
Incense Cedar (Calocedrus)
Calocedrus, commonly known as the Incense Cedar, is a species of conifer in the Cupressaceae family. Three species are native to parts of East Asia, including regions of China, Taiwan, and Japan. One species is native to Northern America. This evergreen tree is valued for its aromatic wood, ornamental appeal, used in traditional medicine, sacred ceremonies and as a timber source. Two Asian species have become very rare, especially in the wild.
Chinese Incense Cedar (Calocedrus macrolepis)
 A medium-size tree up to 25–30 m (65-98 feet) tall. The leaves are scale-like, arranged in flat sprays. The fruit, cones, are small and rounded. Calocedrus macrolepis and Calocedrus formosana are very similar and often confused. The major difference between the two is that the cone stem is shorter on Calocedrus macrolepis, only 0.5 cm long.
A medium-size tree up to 25–30 m (65-98 feet) tall. The leaves are scale-like, arranged in flat sprays. The fruit, cones, are small and rounded. Calocedrus macrolepis and Calocedrus formosana are very similar and often confused. The major difference between the two is that the cone stem is shorter on Calocedrus macrolepis, only 0.5 cm long.
The Chinese Incense Cedar prefers mountainous, well-drained, and slightly acidic soils. They are usually found in mixed forests at moderate to high elevations.
This tree, native to China and the Himalayas, has seen declining populations due to logging and habitat fragmentation.
Taiwan Incense Cedar (Calocedrus formosana)
Also known as the Formosan incense cedar, this species of coniferous tree is found in parts of East Asia, noteably Taiwan. The tree resembles it's Chinese cousin. It typically grows in mountainous forests at elevations ranging from about 1,000 to 2,800 meters. Both varieties are notable for their tall, straight trunk and aromatic, reddish-brown bark.
Deforestation, habitat loss and overharvesting have impacted the populations of the Taiwan Incense Cedar.

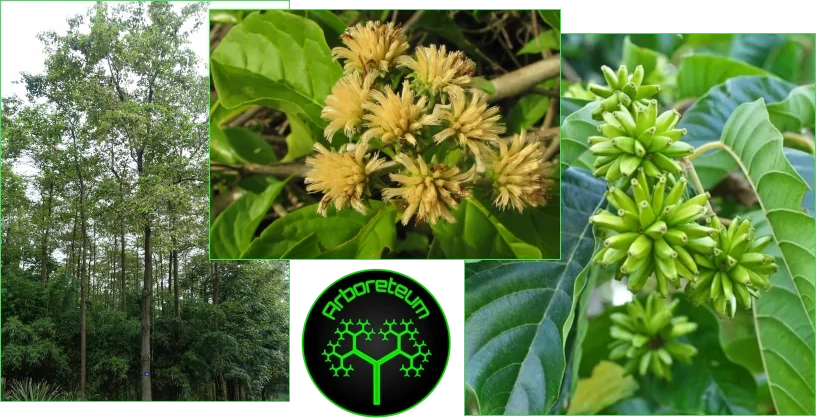
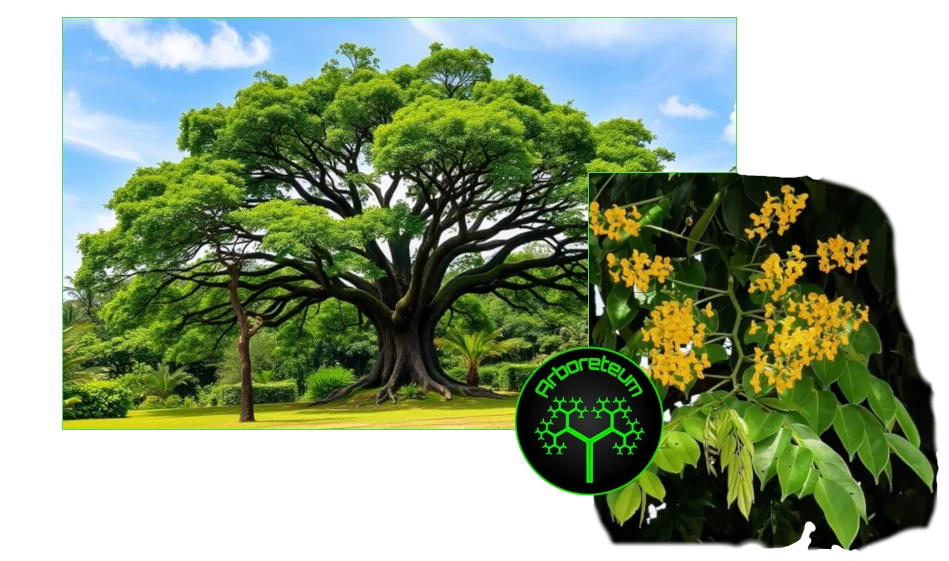
Narra Tree (Pterocarpus indicus)
Pterocarpus indicus, commonly known as the Narra tree, is a species of hardwood tree native to Southeast Asia and the Pacific Islands. It is the national tree of the Philippines. It belongs to the Fabaceae family.
Narra trees typically grow up to 25-40 meters tall, with a broad, spreading canopy. They produce attractive, fragrant flowers that are usually yellow or orange and are often used in traditional medicine and for ornamental purposes. The wood is also notable for its resistance to pests and decay, making it a prized material in woodworking. Narra wood is a reddish colour renowned for its durability.
Pterocarpus indicus holds cultural significance, a symbol of strength and resilience. It is often planted as a shade tree or for reforestation projects.
Sadly the numbers of Narra trees is declining due to unsustainable (often illegal) logging,diseases like Fusarium wilt and habitat loss.

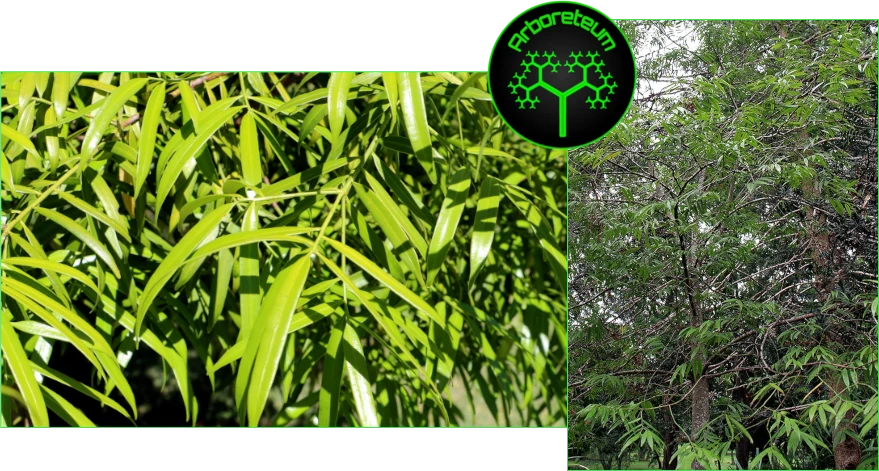
Sundacarpus (Sundacarpus amarus)
Sundacarpus is a small evergreen tree belonging to the family Podocarpaceae. It is commonly found in tropical regions of Southeast Asia, including countries like India, Sri Lanka, and parts of Australia. The plant is known for its hardwood timber and traditional medicinal uses. Its characteristics typically include leathery leaves, small flowers, and woody fruits.
The Sundacarpus is vulnerable due to habitat destruction and it is often targeted for its timber.

Thankfully conservation efforts are underway for many endangered tree species, but continued habitat protection, sustainable logging practices, and reforestation initiatives are critical for their survival.